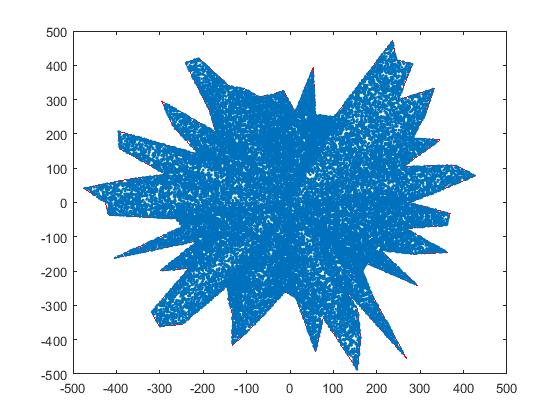
اغلب نواحی که برای شبیه سازی شبکههای بیسیم مورد استفاده قرار میگیرند، نواحی متقارن و عموما مربعی شکل میباشند ، حال آنکه به شکل طبیعی امکان توزیع متقارن نودها وجود نداره، در این پست سعی کردیم که کد توزیع نودها در فضاهای غیرمتقارن را منتشر کنیم، امیدواریم که براتون مفید واقع شده باشه.
در توزیع نودها از روش انتشار نقاط منحنی استفاده شده است.
کد متلب برای توضیحات بالا
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%-----------software details-----------%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
%devloped in Iran(ardebil)
%Copyright (C) 2020(1398) by moussa hasanzadeh as the head devloper %%
%All rights reserved.
%programed in mathlab 2016
%gmail:mo30no@gmail.com
%phone 09147082079
%% clear commands
delete(allchild(0));% delete all figures and graphical objects
clear;% Remove items from workspace, freeing up system memory
clc;% clear the Console
%% path commands
file=matlab.desktop.editor.getActive;% get current script address
try % if dont occur any error this block will run
fileDetail=dir(file.Filename);% get current script details
folderName=fileDetail.folder;% get current script folder name
catch% else if an error occurs then
index=strfind( file.Filename,'\');% find index of back space(\) in path text
folderName=file.Filename(1:index(end)-1);% select all path text from 1 to last Occurrence of \ as script folder name
end
paths=genpath(folderName);% make current path and all sub paths
addpath(paths);% add all paths in known paths of matlab
cd(folderName);% go to path that current script runned from that
%% net building commands
net=[];% create an empty var as net object
net.para.width=1000;% width param of net
net.para.length=1000;% width param of net
net.para.height=5;% width param of net
net.para.side=6;% side of Polygon
net.para.nodNum=1000 ;% number of nodes of net work
net.para.simPer=1000;% number of simulation period
net.para.sInd=0;%period counter
ph=pi/net.para.side;% used for shifting of area to be Attractive!
t=linspace(0,1,net.para.side+1);% Generate linearly spaced vector( used for making polygon)
x1=sin(2*pi*t+ph); x1=(((x1-min(x1))/(max(x1)-min(x1)))-0.5)* net.para.length;% x coordinate of area(after normalising)
y1=-cos(2*pi*t+ph);y1=(((y1-min(y1))/(max(y1)-min(y1)))-0.5)*net.para.width;% y coordinate of area(after normalising)
[x1,y1]=divider(x1,y1,10,1);% adding points between each pair of vertices
rs1=randsample(normalVect(rand(1,length(x1)),1,.5),length(x1));
figure;
x1=x1.*rs1;
y1=y1.*rs1;
[x1,y1]=divider(x1,y1,500);% adding points between each pair of vertices
x1(end+1)=x1(1);
y1(end+1)=y1(1);
plot(x1,y1,'r');hold on
rs=sqrt(randsample(normalVect(rand(1,length(x1)),.0,1),length(x1)));
plot(x1.*rs,y1.*rs,'.')
% give a vector or matrix for normalizing between tow number or 0 and 1
% vect=normalVect([1,-2,4,1,11,4,5])
% vect=normalVect([1,-2,4,1,11,4,5],-2,1)
% vect=normalVect([1,-2,4;11,4,5])
function vect=normalVect(varargin)
if nargin==0
msgbox('give a 1 argoment atleast');
vect=[];
elseif ~isnumeric(varargin{1})
msgbox('abnormal argoment');
vect=[];
else
vect=varargin{1};
if nargin==1
vect=(vect-min(vect(:)))./(max(vect(:))-min(vect(:)));
elseif nargin==3 || nargin>3
if varargin{2}~=varargin{3}
vect=(vect-min(vect(:)))./(max(vect(:))-min(vect(:)));
vMin=min([varargin{2},varargin{3}]);
vMax=max([varargin{2},varargin{3}]);
vDif=vMax-vMin;
vect=(vect*vDif)+vMin;
if nargin>3
msgbox('we used 3 argoment only');
end
else
vect=(vect-min(vect(:)))./(max(vect(:))-min(vect(:)));
msgbox('abnormal limits: normaled 0: 1');
end
end
end
end
%version 1.1
%isFair=1 adding points is based on distance isFair=2 adding of points based on edges
function [X,Y]=divider(X,Y,n,isFair)
try
if isFair==1
else
isFair=0 ;
end
catch
isFair=0;
end
switch isFair
case 0
T1=0;
T2=0;
for i=1:length(X)-1
temp1=0;
temp1=linspace(X(i),X(i+1),n+2) ;
T1=[T1,temp1(1:end-1)];
end
T1=[T1,temp1(end)];
X=T1(2:end);
for i=1:length(Y)-1
temp2=0;
temp2=linspace(Y(i),Y(i+1),n+2) ;
T2=[T2,temp2(1:end-1)];
end
T2=[T2,temp2(end)];
Y=T2(2:end);
case 1
dists= sqrt( (X(2:end)-X(1:end-1)).^2 + (Y(2:end)-Y(1:end-1)).^2) ;
n1=round((dists./min(dists))*n);
T1=0;
T2=0;
for i=1:length(X)-1
temp1=0;
temp1=linspace(X(i),X(i+1),n1(i)+2) ;
T1=[T1,temp1(1:end-1)];
end
T1=[T1,temp1(end)];
X=T1(2:end);
for i=1:length(Y)-1
temp2=0;
temp2=linspace(Y(i),Y(i+1),n1(i)+2) ;
T2=[T2,temp2(1:end-1)];
end
T2=[T2,temp2(end)];
Y=T2(2:end);
end
end
نمونه خروجی برای کد بالا(Output sample for the above code):